lactococcus lactis biochemical test results|Frontiers : Baguio Table Table2 2 shows the results of the fermentation tests. All strains fermented glucose, and all strains of L. lactis subsp. lactis fermented maltose. It had . 7,000 MXN to USD – Mexican Pesos to US Dollars. How much is $7,000.00 – the seven thousand 🇲🇽 mexican pesos is worth $375.49 (USD) today or 💵 three hundred seventy-five us dollars 49 cents as of 11:19AM UTC.We utilize mid-market currency rates to convert MXN against USD currency pair. The current exchange rate is .
lactococcus lactis biochemical test results,Sagar was awarded the SfAM Communications Award 2015: Professional Communicator Category from the Society for Applied . Pure strain sequencing showed results more or less similar to identification methods used for Biochemical tests at species level. A total of 85 pure LAB and 26 .

The phenotypic and biochemical tests recommended by the National Mastitis Committee for the identification of environmental Streptococcus and .
Mesophilic Starters. Lactococcus lactis ( Lc. lactis) is the dominant acidifying mesophile species used, with Leuconostoc mesenteroides ssp. cremoris, a weakly acidifying .
Table Table2 2 shows the results of the fermentation tests. All strains fermented glucose, and all strains of L. lactis subsp. lactis fermented maltose. It had .
Wouters et al. demonstrated reduced glycolytic activity leading to reduced production of lactic acid in Lactococcus lactis at low temperature. According to .

For Lactobacillus crispatus, Lactococcus lactis, and Carnobacterium divergens, the results of biochemical tests showed characteristics similar to those of .a good taxonomic tool for identification of L. lactis subsp. lactis and imply (GTG)5-PCR as a suitable me-thod for identification of other lactococcal species as well as for their .
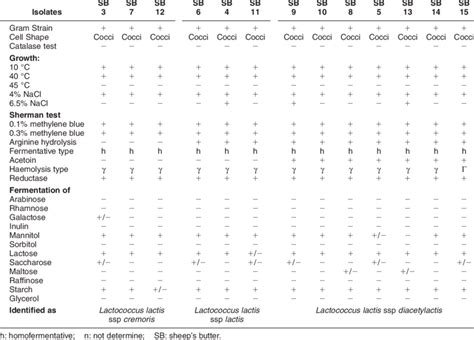
lactococcus lactis biochemical test results Frontiers Abstract. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) comprise a wide range of genera. LAB have been isolated from various sources such as raw and fermented foods, human and .Frontiers In this study we aimed to develop fluorescence-based biosensors to detect diacetyl and acetaldehyde. Since the metabolic pathways for production and .Download Table | Physiological and biochemical characteristics of Lactococcus isolates from publication: Lactic acid bacteria from "Sheep's Dhan", a traditional butter: Isolation, identification .
LACTOCOCCUS REPORT 6 Lactococcus lactis is a gram positive cocci organism which has several significances to humans. The organisms has extensively ben used in the production of cheese and buttermilk since it a ferments milk being a lactic acid bacteria. Besides, the organisms is significant to man since it forms part of the many genetically .
a good taxonomic tool for identification of L. lactis subsp. lactis and imply (GTG)5-PCR as a suitable me-thod for identification of other lactococcal species as well as for their differentiation from enterococci. Further characterization using physiological and biochemical tests confirmed the obtained results and A comparison was made with results of biochemical activity tests and sensitivity patterns to clindamycin and oxacillin. These results were used to construct an improved identification scheme for lactococci from animal origin. . Characteristic Test strip used Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Lactococcus garvieae Table 2. Variable .
Those LAB isolates include six Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus (2), Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (1), . and biochemical tests . Based on the result of identification by preliminary tests, isolates were categorized into various genera. Furthermore, carbohydrate fermentation test was conducted by using . To benchmark the performance of the biosensor to detect diacetyl in bacterial supernatants, 700 μL of filtered L. lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis supernatant were used for induction, or 700 μL of a diacetyl solution (0.42 mM) as control. 500 μL of fresh CDM were added to grow the biosensor cells. Structural and biochemical characterization of in vivo assembled Lactococcus lactis CRISPR-Csm complex Commun Biol. 2022 Mar 29 . Interestingly, comparative crosslinking results indicate a tightening of the Csm3-Csm4 interface as a result of CTR but not NTR binding, reflecting a possible role of protein dynamics change . To prepare the medium, the TSA is cooled, the blood is added aseptically, and then the plates are poured. (1) There are two types of hemolysis. Alpha-hemolysis (α) is caused by damage (but not lysis) of the RBCs in the blood; the media is translucent with a green-ish tinge around the colonies (1). Beta-hemolysis (β) is lysis of the RBCs and . This metabolic model linking the glycolytic flux with pyruvate metabolism via the redox state of the cell obtained with strain L. lactis subs lactis NCDO 2118 (isolated from plant material) was further tested with L. lactis subs. cremoris strains MG1363 and MG1820 (laboratory strains derived from dairy strains), which differ in their ability to .Last updated: August 10, 2022 by Sagar Aryal. Characteristics. Enterococcus faecalis. Gram Staining. Positive. Shape (Cocci/Diplococci/Rods) Cocci. Motility (Motile / Non-Motile) Non-Motile. Inoculate the phenylalanine slant (with a loop on the surface) with a test organism. Note: If you are using the test medium i.e. phenylalanine agar for the first time use positive (Proteus vulgaris) and . For Lactobacillus crispatus, Lactococcus lactis, and Carnobacterium divergens, the results of biochemical tests showed characteristics similar to those of reported probiotics, for example, not . Biochemical test, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and Enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus sequence PCR (ERIC-PCR) were used to compare 42 strains of Lactococcus garvieae . Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis is one of the most important starter bacteria used in dairy technology and it is of great economic importance because of its use in the production of dairy products, including cheese, butter, cream, and fermented milks. Numerous studies have evaluated the biochemical and probiotic properties of .
characteristics. Lactococcus lactis it is a homofermentative bacterium that produces only L-lactic acid when fermenting glucose. It does not form spores. It grows at 10 ° C, but not at 45 ° C. It grows in media with 4% (w / v) NaCl, except L. lactis subsp. cremoris, which only supports salt concentrations of 2% (p / v).. Some of its strains are .Starter cultures usually include Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Lactococcus lactis and yeasts (Chaves-López et al., 2011;Wu et al., 2009a), Lentilactobacillus kefiri, Lactobacillus helveticus .
Formation and conversion of oxygen metabolites by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis ATCC 19435 under different growth conditions. van Niel EW, Hofvendahl K, Hahn-Hagerdal B: Appl Environ Microbiol: 10.1128/AEM.68.9.4350-4356.2002: 2002 * Cultivation: Physiological role of beta-phosphoglucomutase in Lactococcus lactis. Levander F, .lactococcus lactis biochemical test results Pure strain sequencing showed results more or less similar to identification methods used for Biochemical tests at species level. A total of 85 pure LAB and 26 yeast strains were isolated and identified with most abundant species of Lc. lactis ssp. lactis, Lb. plantarum and S. cerevisiae compared with other members of the isolated organisms.
lactococcus lactis biochemical test results|Frontiers
PH0 · Lactococcus lactis, a bacterium with probiotic functions and
PH1 · Lactococcus Lactis
PH2 · Isolation and Identification of Lactic Acid Bacteria
PH3 · Isolation and Characterization of Lactobacillus crispatus,
PH4 · Identification and Typing of Lactococcus lactis by Matrix
PH5 · Identification and Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria in a
PH6 · Frontiers
PH7 · Characterization of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Isolated from
PH8 · Biochemical and molecular identification and characterization of lactic
PH9 · Biochemical and molecular identification and characterization of
PH10 · Biochemical Test of Lactobacillus spp.